Graphite electrodes are primarily used in electric arc furnaces (EAFs) and other high-temperature industrial applications, including the production of steel, aluminum, and other metals. Here are some of the main uses of graphite electrodes:
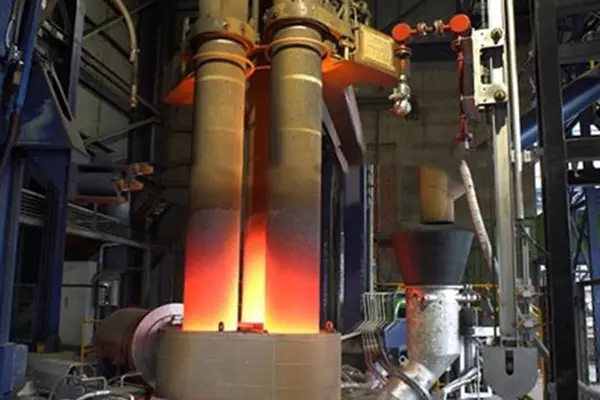
1. Steel Production (Electric Arc Furnace)
- Electric Arc Furnace (EAF): Graphite electrodes are used in EAFs to conduct electricity, which generates the high heat necessary to melt scrap steel and other materials to produce new steel. Graphite’s ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading makes it ideal for this purpose.
2. Aluminum Production
- Electrolytic Cells: In the production of aluminum, graphite electrodes are used in electrolytic cells. Electrolysis is the process of reducing aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) to aluminum metal. The electrodes are used as anode and cathode in the electrolytic bath.
3. Electric Arc Welding
- Graphite electrodes can also be used in certain welding applications, where their high heat resistance and conductive properties are beneficial for making strong, reliable welds.
4. Other High-Temperature Processes
- Production of Silicon and Other Chemicals: Graphite electrodes are used in producing silicon, ferroalloys, and other chemical processes involving high temperatures and electric arcs.
- Non-ferrous Metal Production: They are also used in the production of metals like copper, zinc, and lead.
5. Battery Technology (Emerging Use)
- Supercapacitors and Lithium-ion Batteries: Graphite is a key component in the anodes of lithium-ion batteries and is increasingly being used in supercapacitors due to its conductivity and ability to store electrical charge.
6. Research Applications
- Graphite electrodes are sometimes used in laboratory applications, such as in electrochemical testing, where precise, high conductivity, and corrosion resistance are required.
Graphite’s high thermal and electrical conductivity, along with its ability to withstand extreme temperatures, makes it an essential material for these applications.
Post time: 11-25-2024



